Dear Editor,
Aging involves a series of morphological and functional changes in the kidney.1,2 Although glomerular filtration (GF) decreases with age,3 some studies have tried to relate this slowdown in GF with concomitant diseases such as arterial hypertension (AHTN) and associated cardiovascular disease.4,5 Our objective is to evaluate the degree of GF in the elderly according to the associated comorbidity.
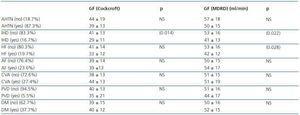
We therefore performed a transversal study coinciding with scheduled visits to the Geriatrics and Nephrology Departments. We included 80 patients who were clinically stable, with an average age of 82.4 ± 6.5 (range 69-97), 68.8% of which were women. From the Geriatrics Department, 38 patients with serum creatinine (Crs) ≤ 1.1mg/dl were included, and 42 from the Nephrology Department with Crs > 1.1mg/dl. The personal antecedents of cardiovascular disease, Diabetes Mellitus (DM) and AHTN are shown in table 1.
Crs levels were determined a week before seeing patients during their scheduled visits and GF was estimated using the Cockroft6 and simplified MDRD formulas.7 Statistics were calculated using the SPSS 11.0 program. Data were expressed in percentage, average and standard deviation. Averages were compared using student’s t-test. The level of significance was 95%.
The overall average GFR estimated using the Cockroft formula is 39.96 ± 14ml/min and the GFR using the MDRD formula is 51.27 ± 16ml/min.
GF levels according to the cardiovascular antecedents analysed are shown in table 1.
Several studies have shown that changes in renal function not only depend on age, but that concomitant cardiovascular disease also contributes to functional changes.4,8 Low GF of the elderly is checked in our study. However, when the GF rate is analysed according to the associated disease, we see how patients with previous history of ischaemic heart disease and heart failure present a lower GF rate. If we also consider that cardiovascular disease is the main cause of mortality in patients with Chronic Renal Failure (CRF),9 that many patients diagnosed with CRF die before having replacement therapy10 and that age cannot be treated, cardiovascular prevention should be a priority in the treatment of chronic renal failure in geriatric patients.
Table 1. Glomerular filtration based on cardiovascular antecedents studied