Dear Editor,
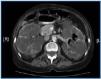
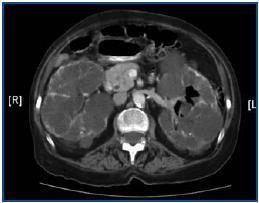
The case of a 70 year old woman is presented that was diagnosed with adult polycystic kidney disease, and that began long term haemodialysis four months earlier. Hospitalization was considered necessary due to the persistence of a constitutional syndrome, resistance to erythropoietin, anaemia, etc. In the anamnesis, the patient described the expulsion of air after urinating, without any other signs or symptoms. A urine culture grew E. coli. In an abdominal Computerised Axial Tomography (CAT) the presence of gas in the bladder and in the left urine collecting system is observed, which is frankly unusual (figure 1). Treatment was started with ciprofloxacin for 12 days and a urethral catheter was inserted, with complete clinical and radiological remission and a negative urine culture.
The enphysematose cystitis is defined as the formation of gas inside of the bladder, which could extend into other parts of the urinary tract.1,2 In general, the clinical manifestations are related to voiding, with haematuria and hypogastric pain. In at least half of the cases, the patients are diabetic.3 Treatment with antibiotics and a urinary catheter is not always effective, making surgery necessary in certain occasions,4 depending greatly on the speed of the therapeutical intervention. In our case, the guiding symptomatology of the process helped to resolve the case. We do not know if there is some link between the adult polycystic kidney disease and the presence of emphysematose cystitis, as we have yet to find bibliographic support in this regard. This has been described in patients on haemodialysis.5 The risk of ascending infection in this particular case must be mentioned.
Figure 1.