Resistant hypertension presents a clinical challenge. The efficacy of renal denervation (RDN) as a potential treatment has conflicting data. Multiple randomized controlled trials have been conducted to assess the impact of RDN.
MethodsWe performed systematic search of the PubMed and EMBASE from inception to April 2024 to identify studies comparing various interventions for resistant hypertension. We employed a frequentist network meta-analysis model, utilizing the net-meta module and applying a random effects model in CRAN-R software.
ResultsData of 2553 patients from 20 RCTs was analyzed. Standard mean differences (SMDs) for diastolic blood pressure (DBP) and systolic blood pressure (SBP) were assessed at different time points, including daytime, nighttime, over 24h, and during office visits. Our results demonstrate an improvement in various BP parameters when comparing RDN with sham: daytime DBP (3.46, 95%CI: [1.89–5.02], P<0.0001), nighttime SBP (2.87, 95%CI: [1.43–4.31], P<0.0001), 24-h SBP (2.82, 95%CI: [1.24–4.41], P=0.001), and in-office DBP (2.70, 95%CI: [1.04–4.36], P=0.002). However, no statistically significant difference was found in daytime SBP (3.60, 95% CI: [−0.67–7.87], P=0.10), nighttime DBP (1.65, 95% CI: [−0.57–3.86], P=0.15) and in-office SBP (3.89, 95% CI: [−10.07–17.86], P=0.60) and in 24-h DBP.
ConclusionOur study supports the efficacy of RDN, when combined with antihypertensive treatment when compared to sham treatment, in the management of resistant hypertension.
La hipertensión resistente presenta una dificultad clínica. La eficacia de la denervación renal (DNR) como tratamiento potencial tiene datos contradictorios. Se han realizado múltiples ensayos controlados aleatorizados para evaluar el impacto de la DNR.
MétodosRealizamos una búsqueda sistemática en PubMed y EMBASE desde su inicio a abril de 2024, para identificar los estudios comparativos de diversas intervenciones para la hipertensión resistente. Usamos un modelo de metaanálisis de red frecuentista, utilizando el módulo net-meta y aplicando un modelo de efectos aleatorios en el software CRAN-R.
ResultadosSe analizaron los datos de 2.553 pacientes de 20 ECAs. Se evaluaron las diferencias medias estándar (DME) para presión arterial diastólica (PAD) y presión arterial sistólica (PAS) en diferentes puntos temporales, incluyendo el día, la noche, periodo de 24 horas y durante las visitas a la consulta. Nuestros resultados demuestran una mejora de diversos parámetros de PA al comparar DNR con simulación: PAD diurna (3,46, 95%IC: [1,89-5,02], P < 0,0001), PAS nocturna (2,87, 95%IC: [1,43-4,31], P < 0,0001), PAS de 24 horas (2,82, 95%IC: [1,24- 4,41], P = 0,001), y PAD en consulta (2,70, 95%IC: [1,04-4,36], P = 0,002). Sin embargo, no se encontró diferencia estadísticamente significativa en cuanto a PAS diurna (3,60, 95% IC: [-0,67-7,87], P = 0,10), PAD nocturna (1,65, 95% IC: [-0,57-3,86], P = 0,15) y PAS en consulta (3,89, 95% IC: [-10,07-17,86], P = 0,60) y PAD de 24 horas.
ConclusiónNuestro estudio respalda la eficacia de DNR al combinarse con el tratamiento antihipertensivo, en comparación con el tratamiento simulado en el manejo de la hipertensión resistente.
Hypertension is a significant global risk factor for cardiovascular disease and mortality.1 While most patients can effectively manage their blood pressure through lifestyle adjustments and antihypertensive medications, there exists a subset of patients with resistant hypertension. Resistant hypertension is defined as uncontrolled blood pressure despite the use of three or more antihypertensive drugs, including a diuretic.2 In the US, this condition affects an estimated 12.8% of individuals and substantially increases the risk of target organ damage, cardiovascular events, and mortality.3 Consequently, there is a pressing need for innovative therapeutic approaches. Catheter-based renal denervation (RDN) has emerged as a promising solution for resistant hypertension.4 Renal sympathetic nerves contribute significantly to hypertension by influencing sodium retention, renin release, and renal blood flow.5 Ablating these nerves via endovascular radiofrequency energy delivery offers a novel approach to reducing sympathetic nervous system over activity. Renal denervation has demonstrated to be an effective non-pharmacological treatment for resistant and uncontrolled hypertension in the presence or absence of concomitant antihypertensive therapy.6-8 However, there have been conflicting results regarding the efficacy of renal denervation in resistant hypertension. Initial studies and registries have reported substantial reductions in in-office blood pressure, reductions typically averaging 25–30mmHg.2 Nevertheless, the Symplicity HTN-3 trial, a blinded sham-controlled study, did not demonstrate a significant advantage of RDN over placebo, possibly due to variations in denervation techniques and patient medication compliance.9 Recent sham-controlled trials have addressed the Symplicity HTN-3 trial limitations and demonstrated that RDN reduces 24-h ambulatory systolic blood pressure by approximately 5–10mmHg compared to a sham procedure, both with and without antihypertensive medications.10,11 Therefore, RDN may complement medication therapy for resistant hypertension. Herein, we performed a comprehensive systematic review and updated network meta-analysis to compare the effectiveness of medical therapy, RDN, and their combination in managing resistant hypertension.
MethodsThe search strategy and methodology of our systematic review and network meta-analysis is consistent with PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines. The checklist of these guidelines is shown in Supplemental S1. The methodological quality was assessed using the Assessing the methodological quality of systematic reviews-2 (AMSTAR-2) guidelines checklist. These are reported under Supplemental S2. This review was not registered.
Inclusion criteria for meta-analysis included papers in which patients between 18 and 80 years of age were diagnosed with resistant hypertension, with (1) In-office SBP from 140 to 180mmHg despite a maximum tolerated dose of 3 or more different-class antihypertensive. (2) In-office DBP of at least 90mmHg or higher. (3) 24-h SBP 140–170mmHg. (4) Mean daytime SBP 135–149mmHg or DBP 90–94mmHg and (5) Stable renal artery anatomy on CT angiogram, magnetic resonance angiogram, or renal angiogram within the previous year.
Exclusion criteria for meta-analysis included patients with: (1) Stable or unstable angina or myocardial infarction within the prior 3 months, history of heart failure, atrial fibrillation, transient ischemic attack, or cerebrovascular accident. (2) Renal artery anatomy ineligible for treatment. (3) Renal artery stenting within 3 months. (4) >50% stenosis in a treatable vessel. (5) Presence of fibromuscular dysplasia. (6) Previous renal denervation. (7) Secondary hypertension (Cushing disease, pheochromocytoma, hyperthyroidism, or aldosteronism, etc.). (8) Severe renal artery stenosis (diameter less than 4mm). (9) Patients with eGFR<40mL/min/1.73m2. (10) Pre-randomization serum potassium level at least 5.5mmol/l. (11) Change in BP medication within 4 weeks from randomization. (12) Pregnancy or (13) Comorbidities with limited life expectancy. Patients were required to discontinue prior use of antihypertensives for at least 4 weeks.
Additionally, we excluded case reports, case series, and review articles. A literature search was conducted using the MEDLINE Portal (PubMed and EMBASE utilizing a systematic search strategy by PRISMA mentioned previously for randomized clinical trials and observational studies until April 2024. The search was performed using titles and keywords utilizing Boolean Operators “OR” and “AND” for terms including: “Renal Denervation”, “Antihypertensives”, or “Resistant Hypertension”. The detailed strategy is given in Supplemental S3.
Study selectionOur study selection included randomized clinical trials, pilot trials, prospective and retrospective observational studies that met our inclusion criteria. Authors screened the articles and any potential full-text article that met the screening requirements, was reviewed again as part of the second phase of screening for evaluation of the outcome of interest. The data screening was then reviewed by another author.
Data collection and statistical analysisThe data and baseline characteristics were arranged in binary outcome format for discrete variables and continuous outcomes for continuous variables using Microsoft Excel software. Baseline characteristics and data included age, gender, race, BMI, smoking, diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, stroke/cardiovascular disease, obstructive sleep apnea, peripheral arterial disease, coronary artery disease, in-office systolic and diastolic blood pressure, 24-h systolic and diastolic blood pressure, morning systolic and diastolic blood pressure, daytime systolic and diastolic blood pressure, nighttime systolic and diastolic blood pressure, in-office heart rate, 24-h heart rate, duration of hypertension, use of antihypertensive medications (including angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, direct renin blockers, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, diuretics, vasodilators, alpha 1 blockers, or centrally acting sympatholytic), serum creatinine, and estimated GFR. Data collection also included the type of blinding in the study design, country of study conduction, and duration of follow-up in study populations.
The outcomes studied were divided into primary and secondary outcomes. Primary outcomes included mean change in in-office blood pressure, along with, 24-h, morning, daytime, and nighttime systolic and diastolic blood pressure at 3–6 months from baseline with RDN in comparison to either antihypertensives alone or sham. While secondary outcomes included mean change in in-office, 24-h, morning, daytime, and nighttime systolic and diastolic blood pressure at 6–12 months from baseline with RDN compared to antihypertensives combined with either sham or RDN alone. Treatments were divided into the following categories:
- 1)
Renal denervation and anti-hypertensive medication
- 2)
Sham and anti-hypertensive medication
- 3)
Anti-hypertensive medication
- 4)
Renal denervation
- 5)
Sham
We report the mean with standard deviations (SD) for baseline characteristics and study outcomes as extracted from the included clinical studies and randomized clinical trials. Statistical analysis was conducted by CRAN-R software (The R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria). A netmeta module was used along with the random-effects model to pool the pre-calculated standard mean differences (SMD) along with standard errors (SE) with a probability value of P<0.05 considered to be statistically significant. The overall net graph for this was also reported. Outcomes were reported as standard mean difference (SMD) with 95% confidence interval (CI). Since sham was used as a reference against which the efficacies of all other strategies were compared, it was given an RR (Risk Ratio) of 0.00. Treatments were ranked based on P values from a netrank module. We also did pairwise comparisons of treatment nodes using inverse variance and DerSimonian–Laird method to estimate between study variance.12 Higgins I-squared (I2) was determined as a measure of statistical heterogeneity where values of ≤50% corresponded to low to moderate heterogeneity while values ≥75% indicated high heterogeneity. The potential inconsistencies between the direct and indirect evidence within the network were evaluated by using the design by treatment approach. Assessment of global inconsistencies was done using a generalized Cochran's Q statistic and local inconsistencies by using the “separate the indirect from direct design evidence’ approach”.13 Publication bias was assessed by visually inspecting a funnel plot and mathematically using the Egger's test. The quality assessment for the included studies was performed using Cochrane Risk of Bias for the randomized clinical trials.14
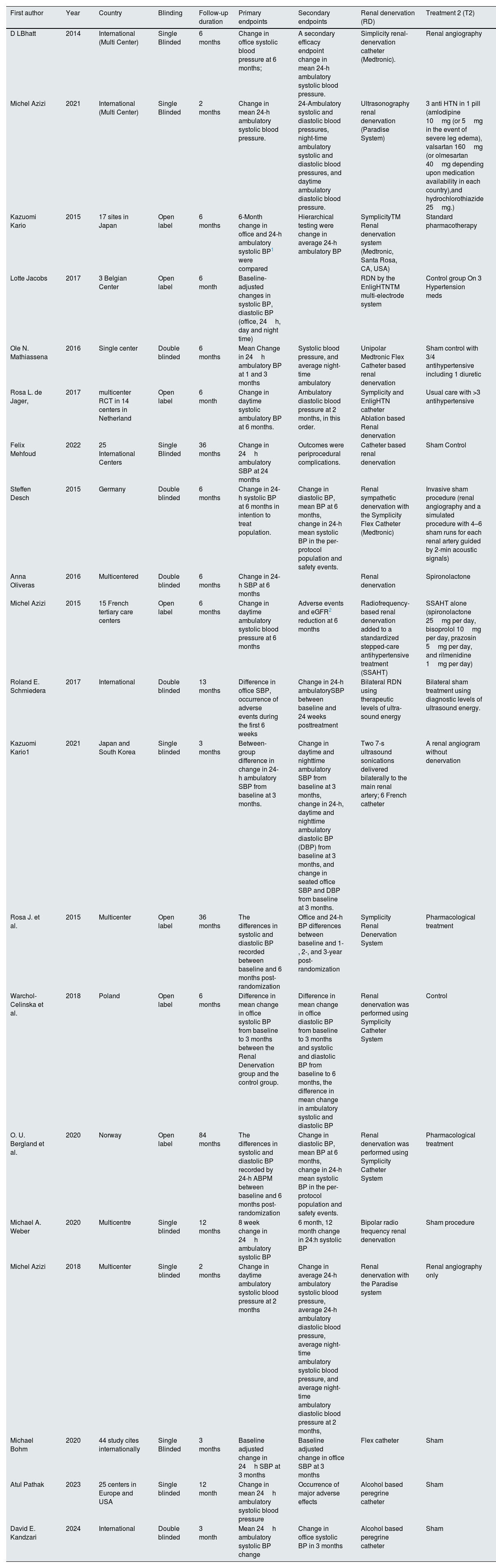
ResultsStudy selection, trial characteristics, and quality assessmentAn initial search of the PubMed/Medline and Embase databases yielded a total of 948 articles (PubMed: 191, Embase: 757). After exclusion based on the title, abstract and full text, a total of 20 randomized clinical trials (RCTs) were deemed eligible for inclusion in our meta-analysis6,15–30 (Fig. 1). The studies varied in sample size, experimental design, patients’ characteristics, and follow-up duration. (Reported in Table 1 and Supplementary 4.) The follow-up duration in most of the included studies was 6 months while in other studies it ranged from 2 to 36 months. The net graph is shown in Fig. 2 which is well connected. The results of this meta-analysis are presented as detailed forest plots (Figs. 1–8 in Supplementary S4 and Fig. 3A and B) and funnel plots with Egger's p test values (Supplemental S5). Three of the studies were given a full text review but not included in the trial as two of them compared types of renal denervation with each other31,32 and one of them had no comparison group.33
Characteristics of included studies.
| First author | Year | Country | Blinding | Follow-up duration | Primary endpoints | Secondary endpoints | Renal denervation (RD) | Treatment 2 (T2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D LBhatt | 2014 | International (Multi Center) | Single Blinded | 6 months | Change in office systolic blood pressure at 6 months; | A secondary efficacy endpoint change in mean 24-h ambulatory systolic blood pressure. | Simplicity renal-denervation catheter (Medtronic). | Renal angiography |
| Michel Azizi | 2021 | International (Multi Center) | Single Blinded | 2 months | Change in mean 24-h ambulatory systolic blood pressure. | 24-Ambulatory systolic and diastolic blood pressures, night-time ambulatory systolic and diastolic blood pressures, and daytime ambulatory diastolic blood pressure. | Ultrasonography renal denervation (Paradise System) | 3 anti HTN in 1 pill (amlodipine 10mg (or 5mg in the event of severe leg edema), valsartan 160mg (or olmesartan 40mg depending upon medication availability in each country),and hydrochlorothiazide 25mg.) |
| Kazuomi Kario | 2015 | 17 sites in Japan | Open label | 6 months | 6-Month change in office and 24-h ambulatory systolic BP1 were compared | Hierarchical testing were change in average 24-h ambulatory BP | SymplicityTM Renal denervation system (Medtronic, Santa Rosa, CA, USA) | Standard pharmacotherapy |
| Lotte Jacobs | 2017 | 3 Belgian Center | Open label | 6 month | Baseline-adjusted changes in systolic BP, diastolic BP (office, 24h, day and night time) | RDN by the EnligHTNTM multi-electrode system | Control group On 3 Hypertension meds | |
| Ole N. Mathiassena | 2016 | Single center | Double blinded | 6 months | Mean Change in 24h ambulatory BP at 1 and 3 months | Systolic blood pressure, and average night-time ambulatory | Unipolar Medtronic Flex Catheter based renal denervation | Sham control with 3/4 antihypertensive including 1 diuretic |
| Rosa L. de Jager, | 2017 | multicenter RCT in 14 centers in Netherland | Open label | 6 month | Change in daytime systolic ambulatory BP at 6 months. | Ambulatory diastolic blood pressure at 2 months, in this order. | Symplicity and EnligHTN catheter Ablation based Renal denervation | Usual care with >3 antihypertensive |
| Felix Mehfoud | 2022 | 25 International Centers | Single Blinded | 36 months | Change in 24h ambulatory SBP at 24 months | Outcomes were periprocedural complications. | Catheter based renal denervation | Sham Control |
| Steffen Desch | 2015 | Germany | Double blinded | 6 months | Change in 24-h systolic BP at 6 months in intention to treat population. | Change in diastolic BP, mean BP at 6 months, change in 24-h mean systolic BP in the per-protocol population and safety events. | Renal sympathetic denervation with the Symplicity Flex Catheter (Medtronic) | Invasive sham procedure (renal angiography and a simulated procedure with 4–6 sham runs for each renal artery guided by 2-min acoustic signals) |
| Anna Oliveras | 2016 | Multicentered | Double blinded | 6 months | Change in 24-h SBP at 6 months | Renal denervation | Spironolactone | |
| Michel Azizi | 2015 | 15 French tertiary care centers | Open label | 6 months | Change in daytime ambulatory systolic blood pressure at 6 months | Adverse events and eGFR2 reduction at 6 months | Radiofrequency-based renal denervation added to a standardized stepped-care antihypertensive treatment (SSAHT) | SSAHT alone (spironolactone 25mg per day, bisoprolol 10mg per day, prazosin 5mg per day, and rilmenidine 1mg per day) |
| Roland E. Schmiedera | 2017 | International | Double blinded | 13 months | Difference in office SBP, occurrence of adverse events during the first 6 weeks | Change in 24-h ambulatorySBP between baseline and 24 weeks posttreatment | Bilateral RDN using therapeutic levels of ultra-sound energy | Bilateral sham treatment using diagnostic levels of ultrasound energy. |
| Kazuomi Kario1 | 2021 | Japan and South Korea | Single blinded | 3 months | Between-group difference in change in 24-h ambulatory SBP from baseline at 3 months. | Change in daytime and nighttime ambulatory SBP from baseline at 3 months, change in 24-h, daytime and nighttime ambulatory diastolic BP (DBP) from baseline at 3 months, and change in seated office SBP and DBP from baseline at 3 months. | Two 7-s ultrasound sonications delivered bilaterally to the main renal artery; 6 French catheter | A renal angiogram without denervation |
| Rosa J. et al. | 2015 | Multicenter | Open label | 36 months | The differences in systolic and diastolic BP recorded between baseline and 6 months post-randomization | Office and 24-h BP differences between baseline and 1-, 2-, and 3-year post-randomization | Symplicity Renal Denervation System | Pharmacological treatment |
| Warchol-Celinska et al. | 2018 | Poland | Open label | 6 months | Difference in mean change in office systolic BP from baseline to 3 months between the Renal Denervation group and the control group. | Difference in mean change in office diastolic BP from baseline to 3 months and systolic and diastolic BP from baseline to 6 months, the difference in mean change in ambulatory systolic and diastolic BP | Renal denervation was performed using Symplicity Catheter System | Control |
| O. U. Bergland et al. | 2020 | Norway | Open label | 84 months | The differences in systolic and diastolic BP recorded by 24-h ABPM between baseline and 6 months post-randomization | Change in diastolic BP, mean BP at 6 months, change in 24-h mean systolic BP in the per-protocol population and safety events. | Renal denervation was performed using Symplicity Catheter System | Pharmacological treatment |
| Michael A. Weber | 2020 | Multicentre | Single blinded | 12 months | 8 week change in 24h ambulatory systolic BP | 6 month, 12 month change in 24:h systolic BP | Bipolar radio frequency renal denervation | Sham procedure |
| Michel Azizi | 2018 | Multicenter | Single blinded | 2 months | Change in daytime ambulatory systolic blood pressure at 2 months | Change in average 24-h ambulatory systolic blood pressure, average 24-h ambulatory diastolic blood pressure, average night-time ambulatory systolic blood pressure, and average night-time ambulatory diastolic blood pressure at 2 months, | Renal denervation with the Paradise system | Renal angiography only |
| Michael Bohm | 2020 | 44 study cites internationally | Single Blinded | 3 months | Baseline adjusted change in 24h SBP at 3 months | Baseline adjusted change in office SBP at 3 months | Flex catheter | Sham |
| Atul Pathak | 2023 | 25 centers in Europe and USA | Single blinded | 12 month | Change in mean 24h ambulatory systolic blood pressure | Occurrence of major adverse effects | Alcohol based peregrine catheter | Sham |
| David E. Kandzari | 2024 | International | Double blinded | 3 month | Mean 24h ambulatory systolic BP change | Change in office systolic BP in 3 months | Alcohol based peregrine catheter | Sham |
This table shows characteristics of included trials, the year of study conduction, the first author, the type of blinding, the intervention groups, the primary and secondary endpoints and duration of follow up.
1. Blood pressure. 2. Glomerular Filtration Rate.
Net diagram. This figure shows a network diagram to show the connection and strength of direct evidence in our outcomes. The width of the edges corresponds to the strength of the direct evidence (estimated by number of studies) between the treatment modalities which are represented by nodes.
Outcomes of renal denervation and antihypertensives in patients with resistant hypertension. (A) Forest plots showing diastolic blood pressure outcomes (DBP=diastolic blood pressure, SMD=standardized mean difference, HTN=hypertension, CI=confidence interval). (B) Forest plots showing systolic blood pressure outcomes (SBP=systolic blood pressure, SMD=standardized mean difference, HTN=hypertension, CI=confidence interval).
Daytime systolic blood pressure: Our pooled analysis demonstrated that there was no statistically significant difference in SBP among group 1 patients undergoing RDN and antihypertensives (3.60, 95% CI: [−0.67–7.87], P=0.10), in group 2 patients undergoing sham and antihypertensives (−2.93, 95%CI: [−7.72–1.86], P=0.23) and group 3 patients with antihypertensives (−1.49, 95%CI: [−4.72–1.73], P=0.37). There was significant reduction in daytime SBP in group 4 patients undergoing renal denervation alone (4.78, 95%CI: [3.10–6.47], P<0.0001). There was a significantly high heterogeneity (I2=96.8%) across these studies.
Daytime diastolic blood pressure: Our analysis showed a substantial reduction in daytime DBP among group 1 patients (3.90, 95% CI: [0.58–7.22], P=0.02), and group 4 patients (3.46, 95%CI: [1.89–5.02], P<0.0001) compared to group 2 (1.41, 95%CI: [−2.30–5.13], P=0.46), group 3 (0.42, 95%CI: [−2.16–2.99], P=0.75), and group 5 patients (0.00) A significantly high heterogeneity (I2=95.4%) was found across these studies.
Nighttime systolic blood pressure: Our analysis showed a statistically significant decrease in nighttime SBP among group 1 patients (5.31, 95% CI: [1.57–9.04], P=0.005), and group 4 patients (2.87, 95%CI: [1.43–4.31], P<0.0001), in comparison to group 2 (2.80, 95%CI: [−1.49–7.10], P=0.20), group 3 (−0.30, 95%CI: [−3.15–2.55], P=0.84), group 5 patients (0.00). We found a significantly high heterogeneity (I2=93.2%) across these studies.
Nighttime diastolic blood pressure: Our analysis showed a statistically significant decrease in nighttime DBP among group 1 patients (4.78, 95% CI: [0.21–9.34], P=0.04) compared to group 2 patients (2.74, 95%CI: [−2.42–7.90], P=0.30), group 3 (−0.10, 95%CI: [−3.63–3.44], P=0.96), group 4 (1.65, 95%CI: [−0.57–3.87], P=0.20), and group 5 patients (0.00). There was a significantly high heterogeneity (I2=97.4%) across these studies.
24-h systolic blood pressure: Our analysis demonstrated a statistically significant reduction in 24-h SBP among group 1 patients (5.67, 95% CI: [1.67–9.68], P=0.006), and group 4 patients (2.82, 95%CI: [1.24–4.41], P=0.001). However, no statistical difference in group 2 (−0.65, 95%CI: [−5.12–3.81], P=0.78), group 3 (0.63, 95%CI: [−2.45–3.70], P=0.69), and group 5 patients (0.00). There was a significantly high heterogeneity (I2=96.2%) across these studies.
24-h diastolic blood pressure: Our analysis demonstrated a statistically significant decrease in 24-h DBP among group 1 (5.88, 95% CI: [3.02–8.74], P<0.0001), group 2 (4.24, 95%CI: [0.97–7.51], P=0.011), and group 3 patients (2.31, 95%CI: [0.10–4.52], P=0.04). There was no statistically difference found in group 4 (0.68, 95%CI: [−0.41–1.78], P=0.22), and group 5 patients (0.00). A significantly high heterogeneity (I2=97.1%) was found across these studies.
In-office systolic blood pressure: Our analysis revealed no statistically significant change in in-office SBP among group 1 (3.89, 95% CI: [−10.07–17.86], P=0.60), group 2 (−1.02, 95%CI: [−17.80–15.74], P=0.91), group 3 (−2.99, 95%CI: [−13.97–8.00], P=0.59), and group 5 patients (0.00). However, there is statistically significant reduction in in-office SBP in group 4 patients (6.09, 95%CI: [0.20–11.98], P=0.04). There was significantly high heterogeneity (I2=99.7%) across these studies.
In-office diastolic blood pressure: Our analysis also revealed a statistically significant decrease in in-office DBP among group 1 (4.95, 95% CI: [0.63–9.28], P=0.03), and group 4 patients (2.70, 95%CI: [1.04–4.36], P=0.002) compared to group 2 (1.54, 95%CI: [−3.63–6.70], P=0.56), group 3 (0.98, 95%CI: [−2.35–4.31], P=0.56), and group 5 patients (0.00). There was significantly high heterogeneity (I2=98.3%) across these studies.
High heterogeneity was observed across all outcomes. This could be explained by the different types of renal denervation used, the difference in follow up duration and the difference in antihypertensive medication regimen and dose.
The risk of bias assessment for included trials is given in Supplemental S6. Furthermore, we included pairwise comparisons of treatment groups in Supplemental S7. The graphs of Fig. 4 show outcomes of pairwise comparison of RDN with sham and of RDN and antihypertensives with sham and antihypertensives. In the comparison of renal denervation and antihypertensive versus sham and anti-hypertensive, the SMD was 1.53(95% CI: 0.63–2.42) for 24h DBP, 6.59 (95% CI: 2.61–10.6) for 24h SBP and 2.35 (95% CI: 1.01–3.70) for daytime DBP. However, in most of pairwise comparisons heterogeneity was high. The direct and indirect estimates of assessed outcomes are shown in Supplemental S8.
Moreover, the p-score ranking of treatment groups in all outcomes is depicted in bar charts in Supplemental S9. The treatment group of renal denervation and antihypertensive medication ranked highest in 24h DBP, 24h SBP, nighttime DBP, daytime DBP, office DBP and nighttime SBP. The results of Higgin's I squared for heterogeneity are given in Supplemental S10.
DiscussionThe management of resistant hypertension remains a challenge in clinical practice, and various therapeutic interventions have been explored to achieve better blood pressure control.34 Among these interventions, RDN has emerged as a potential treatment option.35 This network meta-analysis aimed to systematically evaluate the efficacy of RDN, employed alone in conjunction with antihypertensive medications, in patients with resistant hypertension.
A previous meta-analysis compares RDN with anti-hypertensives and has concluded that RDN is a superior in blood pressure reduction.36 Another recent meta-analysis has compared RDN with sham procedure and its finding revealed that RDN reduced ambulatory blood pressure and daytime systolic blood pressure significantly.37 Although earlier meta-analyses have been published on this objective,38 we utilized a netmeta module to provide more definitive results with more inclusive treatment categories. Our meta-analysis includes the comparison of RDN and antihypertensive combination compared to RDN or antihypertensives alone, upon which pooled effect from different trials has not been compared before.
Our findings revealed several significant findings in blood pressure measurements and outcomes with an RDN alone and with a combination of RDN and antihypertensive medications. These statistically significant reductions underscore the potential clinical significance of RDN as an adjunctive therapy for resistant hypertension.
A significant reduction in daytime DBP suggests that treatment with both RDN alone and as an adjunctive therapy to anti-hypertensives leads to better control of DBP during waking hours. However the daytime SBP was found to be significantly reduced with RDN alone. This improvement translates into a reduced risk of cardiovascular events and target organ damage associated with hypertension.39 Additionally, nighttime hypertension is a known risk factor for adverse cardiovascular outcomes40 and our analysis revealed a substantial reduction in nighttime SBP and DBP with the adjunctive treatment of RDN and antihypertensive therapy. This finding is particularly noteworthy as it addresses the need for effective nighttime blood pressure management in patients with resistant hypertension. Furthermore, 24-h systolic and diastolic blood pressure showed reductions with the adjunctive treatment of RDN and anti-hypertensives. These findings underscore the sustained efficacy of RDN and anti-hypertensives over a day, potentially mitigating the risks associated with fluctuations in blood pressure levels.41 Additionally, RDN and anti-hypertensives demonstrated a substantial reduction in-office SBP and DBP. Our results suggest that RDN, in conjunction with antihypertensive therapy, can lead to improved blood pressure control during healthcare visits, which may enhance patient compliance and satisfaction.42
The findings of this network meta-analysis provide robust evidence supporting the efficacy of RDN in conjunction with antihypertensive treatment for the management of resistant hypertension. The significant reductions in blood pressure observed throughout the day, including daytime, nighttime, 24-h monitoring, and in-office measurements, suggest that RDN when combined with antihypertensive medications, offers a promising approach to managing resistant hypertension. These results are consistent with a growing body of research that underscores the potential of RDN as a valuable adjunctive therapy in this challenging clinical scenario, especially for patients who struggle to achieve blood pressure control with conventional treatments. However, it is crucial to interpret these findings with a consideration of certain limitations.
Firstly, as this is a study-level meta-analysis, addressing individual confounding was difficult due to the lack of patient-specific data. Secondly, there was notable variance in the duration of the follow-up period across the included studies, which may have contributed to the observed heterogeneity in our analysis.
Furthermore, individual patient characteristics, diverse medication regimens, and long-term safety considerations necessitate further investigation. Variability in patient responses, potential adverse effects, and the durability of the observed blood pressure reductions should be carefully evaluated. The included trials have compared anti-hypertensives with RDN but the number, dosage and type of anti-hypertensive medication is not entirely same. A personalized approach considering these factors is essential when considering RDN as a therapeutic option for patients with resistant hypertension. Further research, including long-term follow-up and assessment of safety and adverse events, is warranted to establish the role of RDN definitively in the management of resistant hypertension, and clinical trials are needed to validate these findings and provide comprehensive guidance for clinicians managing patients with resistant hypertension.
In conclusion, clinical trials demonstrating long-term effects in decreasing blood pressure in individuals with stage I–II hypertension who have never received treatment, a modest risk factor profile, and sympathetic over-activity will further determine the future of RDN.43 By focusing on these individuals, comorbidities and irreversible target organ damage—such as conduit artery stiffness and microcirculation remodeling—would be eliminated. The patients can be maintained off pharmaceuticals, preventing ambiguity from non-adherence and changes in drug therapy, because current guidelines suggest lifestyle interventions for these patients for a few weeks to months.41 The procedure's safety may provide another justification for the ethics of these experiments. Such trials, potentially stratified by the RDN system or energy delivery site, might establish or eliminate RDN as a method for treating resistant hypertension.
ConclusionThe results of our study revealed that RDN in combination with antihypertensive medications can be used in the management of resistant hypertension. Our network meta-analysis demonstrated substantial evidence supporting the efficacy of RDN, when combined with antihypertensive treatment, with significant reduction in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure measurements at different time points. These findings align with the recent research highlighting the role of RDN as a potential adjuvant therapy option in patients with resistant hypertension. Patients who have struggled to achieve adequate blood pressure control with conventional treatments may particularly benefit from this approach. However, individual patient characteristics, medication regimens, and long-term safety considerations warrant further investigation. Further research and clinical trials are needed to validate these findings.
Conflict of interestAll authors have nothing to declare.
None.